Operating pressure plays a direct role in controlling the deposition rate of the sputtered material onto the substrate. At low pressures, the mean fre...
READ MORENingbo Danko Vacuum Technology Co., Ltd. Since 2020
As China Vacuum pump Manufacturers and Vacuum pump Suppliers, Danko Vacuum Technology Co., Ltd is committed to expanding our market boundaries by providing high-quality, high-performance vacuum coating equipment. Our Company is highly focused on after-sales service in Domestic and International markets, providing accurate part processing plans and professional solutions to meet customers' needs.


-
-
The Special Coating Machine is frequently equipped with sophisticated inline viscometers or rheometers that continuously monitor the viscosity of the ...
READ MORE -
The Special Coating Machine incorporates a range of coating methods—such as spray, dip, curtain, and electrostatic coating—that can be selectively emp...
READ MORE -
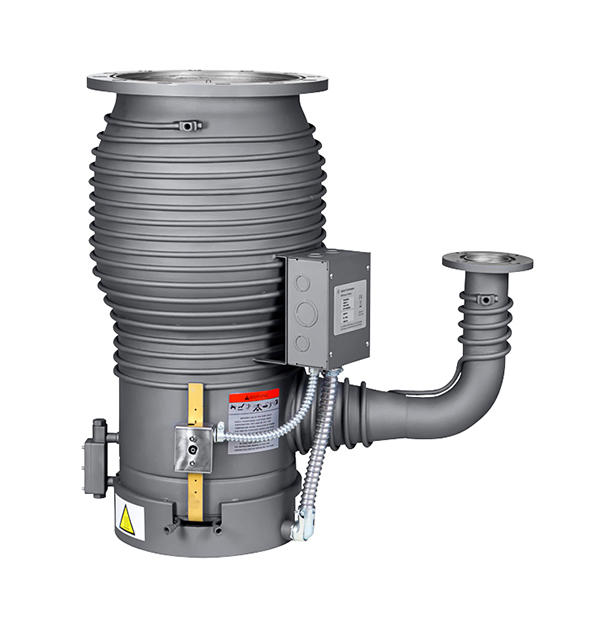
Oil Diffusion Pumps excel at achieving ultra-high vacuum (UHV) levels, typically in the range of 10^-9 to 10^-10 torr. This makes them ideal for appli...
READ MORE
Method for integrating a vacuum pump into a machine control system
Integrating a vacuum pump into a machine control system involves several key steps to ensure smooth operation and effective monitoring. Here’s a general method for achieving this integration:
Define Requirements: Identify the specific requirements for vacuum levels and pump operation based on the machine’s application. Determine how the pump will interact with other components in the system.Select Control Components: Choose appropriate control components, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and sensors for pressure and flow monitoring. Ensure these components are compatible with the vacuum pump’s specifications.
Wiring and Connections: Install the necessary electrical wiring and connections between the vacuum pump, control system, and power supply. Follow safety regulations and standards to ensure proper installation.Install Sensors: Integrate pressure sensors or vacuum gauges to monitor the vacuum levels in real time. These sensors should be connected to the control system to provide feedback for adjustments.
Control Logic Development: Develop control logic within the PLC or control system to manage the operation of the vacuum pump. This may include start/stop commands, variable speed control, and automated adjustments based on sensor feedback.User Interface: Create a user interface on the HMI that allows operators to monitor the vacuum pump’s status, set desired vacuum levels, and receive alerts for any operational issues.
Testing and Calibration: Conduct testing to ensure that the vacuum pump operates correctly within the control system. Calibrate sensors and verify that the control logic responds appropriately to changes in vacuum levels.Safety Features: Implement safety features, such as emergency stop buttons, alarms for low or high vacuum levels, and automatic shutdown procedures in case of faults.
Documentation: Document the integration process, including wiring diagrams, control logic flowcharts, and operating procedures. This documentation will aid in future troubleshooting and maintenance.Training: Train operators and maintenance personnel on the integrated system, emphasizing how to monitor the vacuum pump, adjust settings, and respond to alerts.
Ongoing Monitoring: After integration, continuously monitor the system's performance and make necessary adjustments to optimize the vacuum pump’s operation within the overall machine control system.By following these steps, you can effectively integrate a vacuum pump into a machine control system, enhancing automation and operational efficiency.

 Email:
Email:  Tel:+86-13486478562
Tel:+86-13486478562
 Language
Language  Español
Español Português
Português







 Tel: +86-13486478562
Tel: +86-13486478562 FAX: +86-574-62496601
FAX: +86-574-62496601 Email:
Email:  Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China
Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China